Global Climate News - April 17
Green ammonia and methanol in shipping; EU portal for building energy use and emissions; Scaling offshore wind manufacturing in UK; reducing freight emissions in Canada;
Green ammonia and methanol for shipping
Rocky Mountain Institute & the Global Maritime Forum published research on achieving a target of 5-10% green fuel for shipping by 2030. Key insights:
The cost to transport green ammonia and methanol is low. The final cost of these fuels largely comes from the cost of production of hydrogen, which will be low in places with - high renewable energy potential, low cost of capital, subsidies for hydrogen production
Safety protocols are needed - both ammonia and methanol are toxic. Methanol is also flammable and burns with a flame that cannot be easily seen in daylight
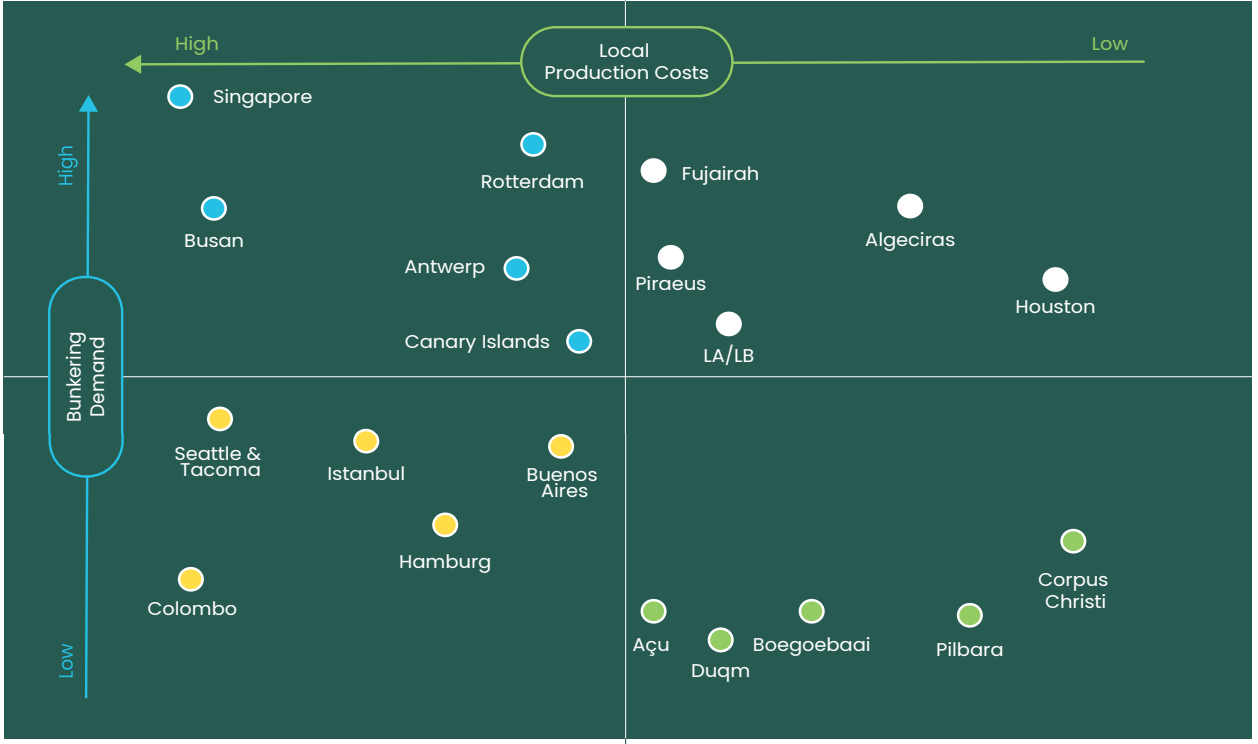
Cost of using ammonia/methanol at ports is driven by production cost (mainly depends on electricity cost), and demand - this affects the unit cost of fuel storage and bunkering
Green methanol supply may be concentrated in EU, major bunkering hubs. Green ammonia supply can be more distributed
Project cost for green ammonia - $900-2700, and for green methanol - $900-2500 - per metric ton VLSFO equivalent by 2030. Expected to be lowest in the US due to credits under the Inflation Reduction Act.
Greatest opportunity in places where production cost is low and demand for bunkering fuel is high (top right quadrant in the picture below)
Offshore Energy | Oceans of Opportunity - Supplying Green Methanol and Ammonia at Ports (PDF) (recommended)
EU Portal for Building Energy & Emissions
EU has updated its Building Stock Observatory (BSO) website that includes information such as energy use and helps assess their GHG emissions. Here’s an overview of buildings in Sweden from the BSO dataset:

EC Press Release | EU Building Stock Observatory
Scaling Offshore Wind Supply Chain in UK
The Crown Estate (UK), which owns the seabed upto 12 nautical miles from UK’s coast, Crown Estate Scotland, and industry groups in the UK plan to triple offshore wind manufacturing capacity in the country over the next decade. The plan has 5 focus areas:
The plan uses a “make or buy” approach to prioritise areas to scale and invest in. The “Make” category is where UK can scale and serve a long-term market.
Recharge | 2024 Offshore Wind Industrial Growth Plan (PDF)
Daily Climate News - April 3
Reliability of technology advances in Solar PV;
US blueprint for decarbonizing buildings;
How important is protecting apes?
Top Stories
A total of 117 GW wind power was commissioned in 2023, with most of it - 75GW - in China. Other leading countries were US, Brazil, Germany and India. About 10.8GW of the capacity was offshore, and the rest - 106GW - onshore. Mercom | Global Wind Report 2024
Pembina Institute has identified few challenges that are keeping fleet operators from switching to electric and hydrogen-powered medium and heavy duty vehicles in Canada:
lack of understanding about the new technologies
installing chargers on-site can be expensive and there aren’t enough public ones
higher electricity rates for EV fleet owners
regulatory barriers
lack of standardisation among chargers
sufficient grid capacity
Construction on the first Small modular reactor in the US is expected to start this year in the state of Wyoming. Terrapower will build a sodium-cooled 345MW reactor, along with a thermal storage system.
Brick manufacturing employs more than a million people in Bangladesh, and contributes nearly 17% to annual CO2 emissions and 11% to PM2.5 emissions, since kilns are coal-fired. “The scale of manufacturing is so great that at some times of year, Dhaka (the capital of Bangladesh) looks like Mordor.” In a pilot, researchers found low-cost ways to reduce coal use in kilns:
stacking the bricks in a way that increases airflow in the kiln and feeding the coal fires more frequently in smaller rather than larger batches
About 1000 brick manufacturers are being trained in these new methods.
Dubai, and several other areas in the Middle East - Bahrain, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Oman - received the highest recorded rainfall in 75 years. The Guardian
In 2019, EU adopted rules that require “grid operators to ensure that at least 70% of their physical transmission capacity is available for cross-border electricity trading by the end of 2025 at the latest”. The EU Agency for Cooperation of Energy Regulators, ACER, has warned that member states need to work together to reduce transmission congestion and “undertake targeted grid developments” to meet the 2025 deadline.
The last ACER report (July 2023) found that most Member States in highly meshed areas of the power grid made available on average 30-50% of the capacity for certain network elements. In parallel, the costs of managing grid congestions in the EU exceeded €4 billion in 2022. ACER
Denmark has awarded contracts to 3 companies to capture and store 160,352 tonnes of CO2 every year from 2026 to 2032. EnergyWatch | Danish Energy Agency
The city of Phoenix (Arizona, USA) aims to increase its canopy cover to 25% by 2030 and is awarding grants for planting and caring for trees. The grantees receive supplies to care for the trees and funds for landscaping services. Both individuals and groups can apply. The Guardian | Arizona Technology Council
You can find all previous posts of this newsletter here.
You can read over 150 stories from April 17 on Telborg.
I’d greatly appreciate you sharing this newsletter on Twitter and LinkedIn.
Let me know if I can help with anything! Enjoy your day!
Best,
Soumya Gupta
Founder, Telborg.com | SummaryWithAI.com
LinkedIn | Twitter | soumya@telborg.com
Global Climate News - April 16
Latvia’s Hydrogen-fueled Trolleybuses;
Replace Palladium with Nickel or not;
Greece's new plan to protect marine areas;
Decarbonizing power generation in Indonesia
Global Climate News - April 13-15
Solar module prices in China;
Drones for protecting biodiversity;
Financing water treatment through carbon markets;
European Solar Charter for onshore solar module manufacturing;
Finland's first synthetic methane plant;
Global Climate News - April 12
Europe's voluntary certification framework for carbon removals;
Pumped hydro storage in Sydney (Australia);
South Africa's Helium-cooled High Temperature Nuclear Reactor;
Hydrogen in the Balkans;









